
Varicocele is One of the Main Causes of Male Infertility You Should Know

Are you worried about this kind of pain in the scrotum that you have never experienced before? Do you find it embarrassing and uncomfortable to at least discuss the pain in your testicles with your doctor? This is probably a symptom of a condition called varicocele.
What is varicocele?
Varicocele basically is an enlargement of veins located within the scrotum especially on the left side and along the spermatic cord, so they appear like tortuous worms located within the scrotum when anyone feels it. The disease is relatively common and about 15% of all men between the ages of 15 – 25 years have Varicocele. The exact cause is not known however it is because of the loosening of valves which normally help in the unidirectional flow, failure of which causes reflux of the blood from the abdomen into the scrotum. The causation is just like varicose veins of the leg.
Primarily varicocele is an abnormal enlargement of veins of the scrotum that forms a sac around the testicles. This condition can reduce the number of sperms, their motility and shape. It causes serious damage to the DNA of the sperm, then it can have adverse effects on fertility. Varicocele sometimes may not show symptoms.
- Varicocele often feels like “a worm bag”.
- The pain caused by varicocele can be moderate to severe depending on its severity and may aggravate when the person is standing for a long time.
- It can cause ineffective/ insufficient sperm production, which can lead to infertility.
Types of varicocele:
There are three types of varicocele
Grade1: This is not visible but feels it by using Valsalva maneuver (take a deep breath and hold it while you bear down).
Grade2: This is not visible but it can be felt without a Valsalva maneuver.
Grade3: This type of varicocele is visible.
How is a varicocele diagnosed?
During a physical exam, The Interventional Radiologist may identify a varicocele based on your symptoms. An ultrasound examination, which can offer more detail about the testicular veins, may be used to confirm a diagnosis.
Can varicocele be prevented?
No medication has been shown to be effective in treating or preventing varicocele. The following tips are suggested to improve your nerve health and protect it so as to prevent varicose veins.
Getting regular exercise, eating a nutritious diet, drinking plenty of water and quitting smoking have all been shown to improve your vascular health.
What are the Interventional Treatments available for Varicocele?
varicocele embolization:
The procedure for varicocele embolization one of the Radiology treatments is done by an Interventional Radiologist in this procedure is usually performed as an outpatient procedure with sedation and local anesthesia. Through a small skin incision, a small catheter (tube) is placed into a leg vein around the hip or neck vein. Under X-ray guidance, this tube is inserted into the varicocele. To confirm the catheter’s location, a little amount of X-ray dye (contrast) is administered. The vein is then implanted with tiny coils made of stainless steel or platinum, balloons, or other materials. They’re used to stop the backflow, or pressure, in the varicocele by blocking it. Blood can still leave the testicle via regular channels. The catheter is removed once it is established that there is no flow in the affected vein. This procedure is usually completed within one hour.
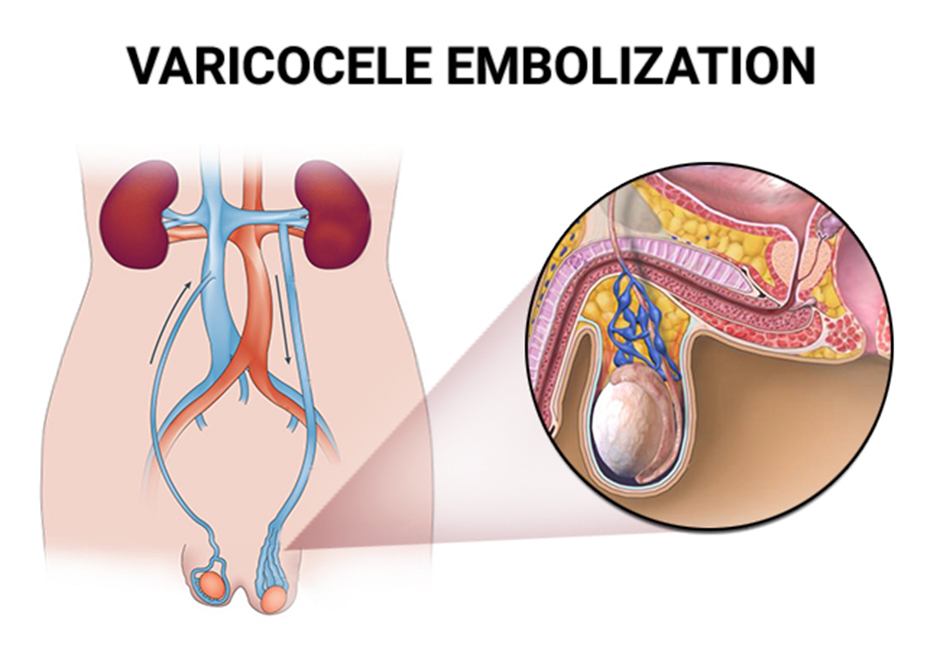
Post-surgical care:
Varicocele embolization is a daycare minimally invasive procedure, wherein the patient comes in and comes out on the same day and he required very minimal post care procedure care
It Involves:
- Avoid physically stressful activities for 4-6 weeks post-surgery
- A minimal pain killer can be given for 1 or 2 days and otherwise doesn’t require any restrictions.
Advantages of varicocele embolization:
- Minimally Invasive
- Local Anaesthesia (No General anesthesia)
- Same-day discharge
- Minimal post-surgery pain
- Minimal Risks
- No Scars
- No Sutures
- No Infections
How does Varicocele Affect Male Fertility?
Male infertility can also be caused by varicoceles. Varicoceles can cause your testicles pressure and temperature to rise. Increased temperature or pressure can block sperm production, and if you have a varicocele, your sperm count may be lower than normal or your sperm may be damaged. Damaged sperm are less mobile, which can make it difficult to conceive. Fortunately, receiving treatment can often help you overcome your problems. After obtaining treatment, many men with varicoceles are able to have children.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Can varicocele be left untreated?
It is always a better option to consult an Interventional radiologist for varicocele. If left untreated, it can lead to infertility, difficulty maintaining an erection, erectile dysfunction, poor sperm quality, and low sperm count, all of which can have a negative impact on one’s quality of life.
Why is varicocele more common on the left side?
Because of the body’s anatomy, varicocele is more common on the left side than the right. Varicocele is more likely to develop on the left side as a result of indirect venous drainage.
How does the testicle look in the varicocele?
The testicle does not change as a result of the varicocele. In severe varicocele patients, however, the veins in the testicles can appear superficial, similar to varicose veins in the legs. Varicose enlarged veins are palpable and visible through the skin.
What is Bilateral Varicocele?
While varicocele is 90% seen in the left testicle, 8-9% can be seen on both sides. The occurrence of varicocele in both sides is named as bilateral.
About the Author:

Name: DR .SURESH GIRAGANI
INTERVENTIONAL RADIOLOGIST
DR. SURESH GIRAGANI CONSULTANT INTERVENTIONAL RADIOLOGIST at Yashoda group of hospitals has more than sixteen years of clinical experience in vascular interventions with a special interest in neurovascular and peripheral vascular disease interventional procedures.