Hepato biliary interventions
Scope of hepatobiliary interventions ?
Hepato biliary interventions compromise a large spectrum of interventional radiology procedures indicated especially in patients with obstructive jaundice, treatment of portal hypertension and its complications. They can be categorised into 3 groups of interventions employed in 3 distinct pathoanatomical entities. These include biliary interventions, interventions for portal hypertension and its complications and interventions for Budd chiari syndrome.
List of hepatobiliary interventions
- 1. Percutaneous transhepatic biliary drainage ( PTBD)
- 2. Percutaneous transhepatic biliary stenting ( PTBD + stenting with SEMS)
- 3. HVPG ( Hepatic venous pressure gradient measurement)
- 4. Transjugular liver biopsy
- 5. Transjugular portosystemic shunt (TIPSS)
- 6. Direct intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (DIPSS)
- 7. Hepatic venoplasty or Hepatic venous stenting for Budd chiari syndrome
- 8. IVC stenting for IVC webs in Budd chiari syndrome
- 9. Balloon retrograde variceal embolization
- 10. Portal vein embolisation for improving functional liver remnant
Biliary interventions - obstructive jaundice
Obstructive jaundice denotes structural lesion either benign or malignant causing obstruction to the biliary tree. ERCP is the first line of management for obstructive jaundice. ERCP may not be feasible in cases of high biliary strictures (cholangiocarcinoma, gallbladder carcinoma with hilar invasion), hepatojejunostomy strictures. In these cases, as well as in cases of failed ERCPs, percutaneous transhepatic biliary access followed by biliary drainage can be done. In cases of inoperable malignant biliary strictures, PTBD + biliary stenting with SEMS ( self expandable metallic stents) can be done
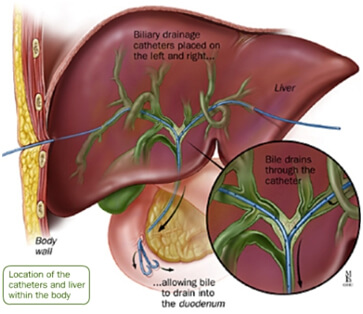
PTBD - procedure - how it is done ?
PTBD ( Percutaneous transhepatic biliary drainage) is done using ultrasound and fluoroscopic guidance to access the biliary ducts and drain them. It is usually done under local anaesthesia or conscious sedation. PTBD can be done as a day care procedure. Depending upon the indication and extent of obstruction, PTBD can be done with external drainage oor internal - external drainage.
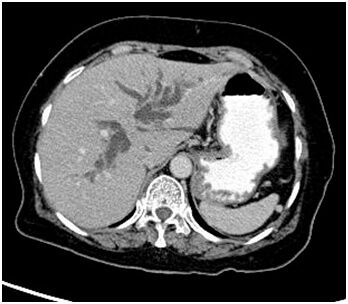
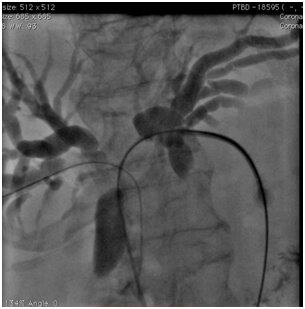
The role of interventions in medically intractable portal hypertension ?
Normally, blood coming from esophagus, stomach, and intestines first flows through the liver. When the liver has a lot of damage and there are blockages, blood cannot flow through it very easily. This is called portal hypertension (increased pressure and backup of the portal vein). The veins can then break open (rupture), causing serious bleeding.
Portal hypertension and its complications ( variceal bleeding, ascitis etc) can be treated by medical management using beta blockers, somatostatins, diuretics etc or by local endoscopic treatments including variceal banding/sclerotherapy . In cases of medically intractable portal hypertension, Interventional treatments can be helpful sometimes life saving. The interventional treatments include
Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic systemic shunt (TIPSS)
Balloon retrograde transvenous occlusion of varices (BRTO)
Selective transvenous embolisation of varices
DR.SURESH GIRAGANI CONSULTANT INTERVENTIONAL RADIOLOGIST at Apollo Hospital, has more than Seventeen years of clinical experience in vascular interventions with a special interest in neurovascular and peripheral vascular disease interventional procedures.
Services
Quick Links
Contact Us
Copyright 2021 Neuro All rights reserved. | Powered By KBK Business Solutions