
Brain Aneurysm Treatment with the latest Intrasaccular (Web and Contour) Devices
What is a Brain Aneurysm?
An aneurysm is actually a defect in one of the arteries in the brain. It represents a weak area in that artery that can be prone to bleeding which can cause a dangerous type of bleeding stroke. Brain aneurysms swelling in blood vessels of the Brain which are similar to balloons that keep swelling of increasing size and burst to cause bleeding in the brain. The bleeding inside the brain can cause significant morbidity or sometimes it can be fatal.
Previously these aneurysms used to be managed by open surgical clipping, of late most of these patients are treated by Interventional/ endovascular methods. Interventional methods including coiling of brain aneurysms can have efficacy and durable issues with aneurysms of particular morphologies.
Recently a new class of endovascular devices called as Intrasaccular (Web and Contour) Devices, to circumvent the problem of treating these technically difficult-to-treat aneurysms.
Why Intrasaccular Devices?
Intrasaccular devices are safe and effective treatment options for wide neck bifurcation aneurysms. It is technically simpler for as compared to stent-assisted coiling as this procedure avoids stents and their associated complications. These treatments are indicated for aneurysms located in the brain’s Middle Cerebral Artery (MCA) bifurcation, Internal Carotid Artery (ICA) terminus, Anterior communicating artery (Acom) Complex or basilar artery apex.
Advantages of Intrasaccular Devices:
• Flow disruption (or) flow diversion.
• No Parent vessel compromise.
• No long-term antiplatelets.
What are the features of a good Intrasaccular device?
• Safe and effective device
• Easy to use
• Easy to deploy
• Easy to size
• Well visible on angiography
• Occlusion rates should match stenting results
Types of Intrasaccular devices?
- WEB
- CONTOUR
- NEQSTENT
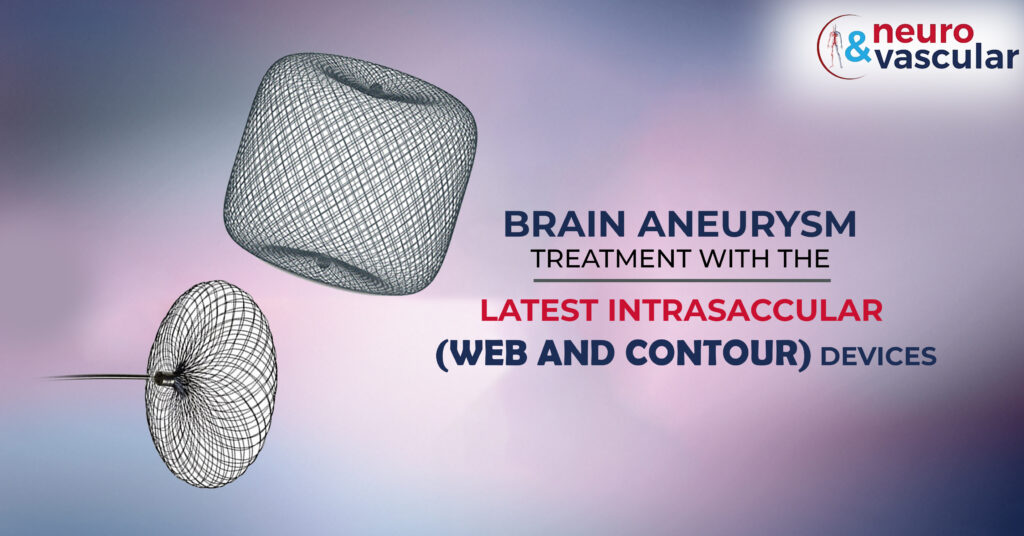
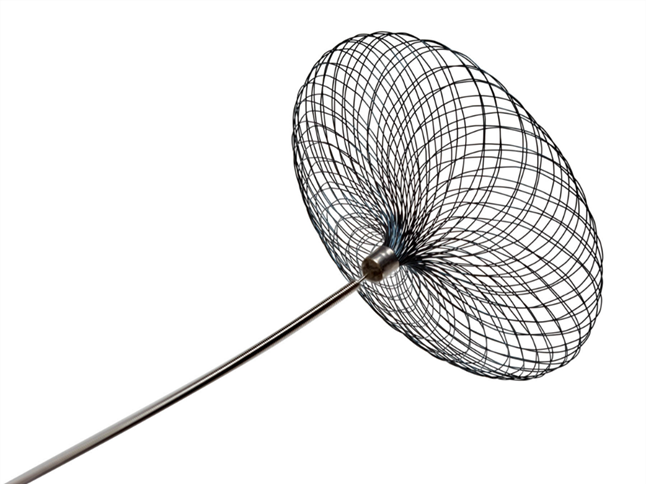
WEB (Woven Endo Bridge) Device:
The Woven Endo Bridge (WEB) Nitinol braided intrasaccular device is the newest technology for treating aneurysms. WEB device is a self-expanding mesh ball that’s implanted at the base of the aneurysm it causes clotting and prevents more blood from entering the bulge preventing a rupture in the brain. The device system consists of the implant, the delivery wire, and the controller that is used to detach the device from the delivery wire. So it’s made out of metal wires of different sizes we can select the WEB device that is appropriate for someone’s specific aneurysm and then place it into the aneurysm during this treatment procedure.
The WEB is indicated for use in aneurysms with a diameter of up to 11mm. The devices range from 3mm up to 11mm and are generally oversized in the aneurysm for best results. The distal and proximal tips of the Web are equipped with radiopaque markers. The nitinol wires are filled with platinum cores making them slightly visible but not blocking visibility as a coil mass would.
There is a radiopaque marker on the top and bottom of the device. The device can be re-sheathed and is detached using a detachment controller.
How is WEB Procedure Performed?
The procedure is performed percutaneously either from the thigh (femoral arterial access) or from the wrist (radial arterial route). A system of 2 long small tubes (Guiding catheter and microcatheter) is navigated into the target artery and the microcatheter (the smaller inner tube/ catheter for delivering the WEB device) is targeted into the aneurysm.
The WEB device is delivered through this microcatheter into the aneurysm under fluoroscopic guidance. Once the optimum position of the device is achieved in the aneurysm, then the device is detached from its pusher wire.

Advantages of WEB Device:
One of the most significant benefits of the WEB is its ability to simplify the procedure in suitable cases which further shortens the procedure times. It can shorten the duration of the patient’s anesthesia, reduce radiation and contrast exposure, and deploy the device to the brain with a single entry, lowering the risk of complications. Patients’ hospital stays and recovery times are also reduced, with many patients able to return home within 24 hours of surgery.
Contour device:
A contour device is an Intrasaccular device indicated to treat bifurcation aneurysms. This device is specially intended to be used in unruptured wide-necked bifurcation aneurysms but can also be used in varying morphologies. The device has a dual-layer nitinol micro-braided mesh containing a platinum core wire for visualization. It is re-searchable and re-deployable (electrolytic detachable). The device is compatible with a 0.027″ microcatheter. Contour Neurovascular System is compatible with a microcatheter 0.027″.
How is Contour Procedure performed?
Similar to WEB device deployment, the Contour procedure can also be performed percutaneously either from the thigh (femoral arterial access) or from the wrist (radial arterial route). A system of 2 long small tubes (Guiding catheter and microcatheter) is navigated into the target artery and the microcatheter (the smaller inner tube/ catheter for delivering the WEB device) is targeted into the aneurysm. The WEB device is delivered through this microcatheter into the aneurysm under fluoroscopic guidance. Once the optimum position of the device is achieved in the aneurysm, then the device is detached from its pusher wire.
Advantages of Contour Device:
The sizing of the device is relatively easy, making procedural planning simple, and the device is stable and relatively safe to use. It is also easy to navigate into the aneurysm using smaller 0.027 microcatheters. Long-term follow-up data will be crucial to assess this novel technology.
Conclusion:
Endovascular treatment of intracranial aneurysms with the WEB & Contour devices are the most recent innovation in the field. When compared to current endovascular therapies for similar aneurysms, this treatment has consistently shown excellent safety and efficacy in several prospective, multicentre studies. Given the procedure’s technical simplicity and efficiency, there will almost certainly be a progressive expansion of indications for IS-FD therapies in the future, to the point where they will eventually replace standard coiling in an increasing number of cases.
About the Author:

Name: DR . SURESH GIRAGANI
INTERVENTIONAL RADIOLOGIST
DR. SURESH GIRAGANI CONSULTANT INTERVENTIONAL RADIOLOGIST at Apollo hospitals Jubilee Hills, has more than sixteen years of clinical experience in vascular interventions with a special interest in neurovascular and peripheral vascular disease interventional procedures.