How To Solve Issues in Liver With Liver Biopsy procedure
The Liver is an extremely important organ. It makes proteins and enzymes that are needed for vital metabolic processes, eliminates contaminants from the blood and improves infection prevention, and stores vitamins and nutrients. Liver problems can make you very sick or even cause death.
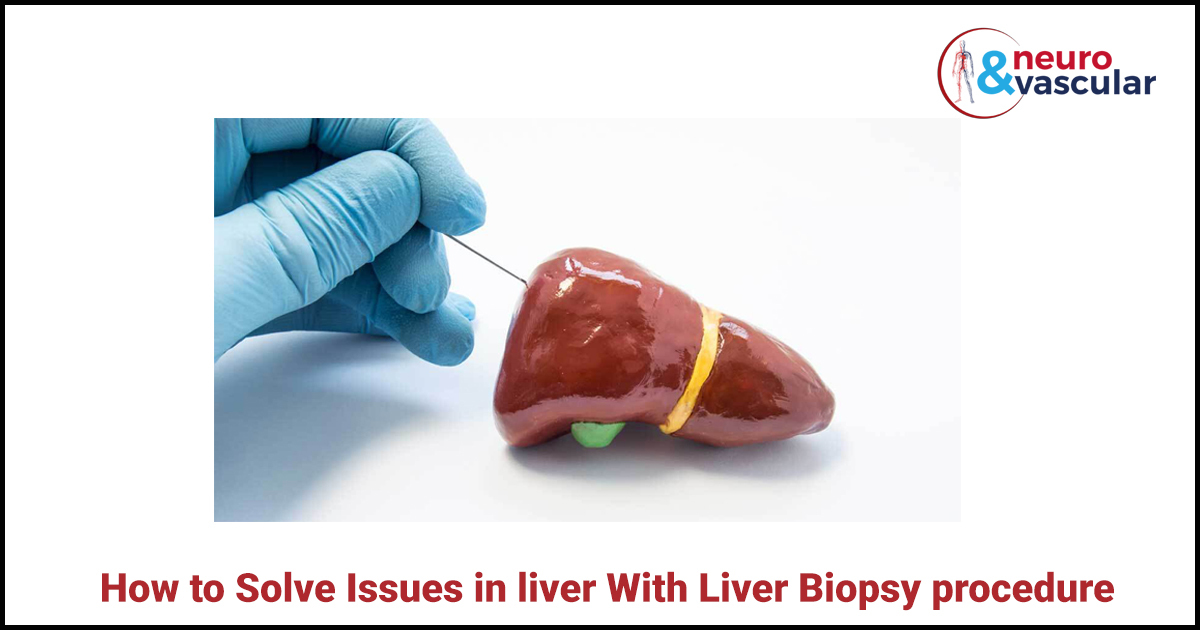
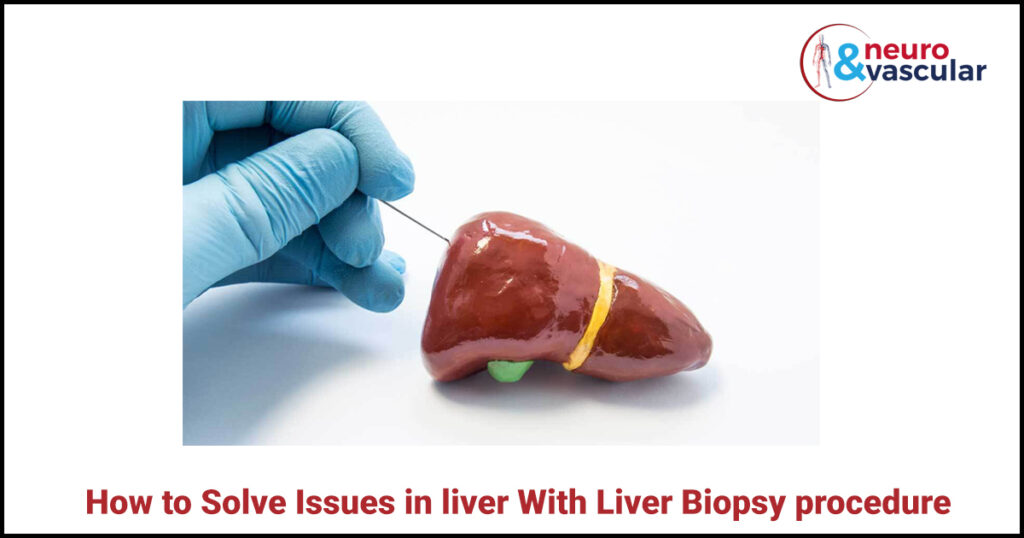
A liver biopsy is a methodology that is performed to extract a sample of the liver tissue. This is performed by inserting a needle between two right lower ribs. The tissue sample that is taken is then sent to the lab and looked at under a microscope to recognize if there are any liver issues.
When the liver parameters in a blood test are abnormal, a liver biopsy is usually performed. It can also be done if an ultrasound, CT scan, or x-ray of your liver reveals an underlying problem.
Why is a liver biopsy performed?
A liver biopsy can also be used to identify the cause of:
- persistent abdominal pain
- Abnormal liver functions
- Unexplained yellowing of the skin Jaundice
- Abnormality of liver found on Ultrasound and CT Scan
- Unexplained Enlargement of the liver
Diseases that may need a Liver Biopsy:
The following are some of the most common liver diseases for which a liver biopsy is conducted.
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
- Chronic hepatitis B or C
- Alcoholic liver disease
- Autoimmune hepatitis
- Primary biliary cirrhosis
- Primary sclerosing cholangitis
- Wilson’s disease
What are the types of Liver Biopsies?
The Abnormality of liver found on Ultrasound (Ultrasound Liver Biopsy) or CT scan (CTGuided liver Biopsy) Diagnosis. By utilizing these Imaging techniques Liver Biopsy is performed by An Interventional Radiologist.
Types of Liver Biopsies:
Percutaneous Liver Biopsy:
This is the most common type of liver biopsy and it is also called a needle Biopsy. In this Biopsy Procedure, an Interventional Radiologist inserts a needle through the abdomen and into the liver.
Transjugular liver Biopsy:
In this Transjugular liver Biopsy(TJLB Liver Biopsy) procedure involves making a small incision at the neck. A thin flexible tube is inserted into the liver through the jugular vein in the neck. People who have bleeding disorders prefer this method.
Laparoscopic liver Biopsy:
In Laparoscopic liver Biopsy is done through a small abdominal incision and is frequently used when samples are needed from a specific area of the liver.
The kind of anesthesia your doctor gives you will rely upon which kind of liver biopsy they perform. The percutaneous and transjugular biopsies use local anesthesia, which means only the affected area is numbed. Laparoscopic biopsies require general anesthesia, so you’ll be in a deep, painless sleep during the procedure.
Preparation Before the procedure:
Any pre-existing medical issues (heart or lung disease), pregnancy, allergies, and all drugs you’re taking should be disclosed to the doctor. If you’re taking blood-thinning drugs like aspirin, warfarin, clopidogrel, or enoxaparin, you should take extra measures Prior to the liver biopsies, tests such as a blood count, platelets, PT(INR), and USG will be conducted.
During the procedure:
- During the procedure, you must lie on your back with your right elbow out to the side and your right hand under your head, and remain as still as possible. an ultrasound scan will be done to evaluate the exact area of your liver.
- The vascular surgeon should use local anesthesia to clean and numb an area on your upper abdomen, then make a small incision over your stomach and insert a needle into your liver to take a small sample of tissue for analysis.
After the procedure:
- For up to 6 hours, you will be kept under surveillance.
- You may have some minor discomfort or pain, and you will be given pain medication if necessary.
- After the biopsy, you should not participate in any excessive physical activity for at least 24 hours.
The advantages of the Liver Biopsy procedure are
- It takes less time to complete.
- It is helpful in differentiating between cancerous and non-cancerous cells.
- Diagnoses a variety of liver issues.
What are the possible risks of a liver biopsy?
Pain: You may have pain at the biopsy site. You could also get pain in your back or right shoulder.
Bleeding: Minor bleeding may occur at the biopsy site or around the liver inside the abdomen.
Infection: Infection rarely develops at the site of the biopsy or in the bloodstream.
Injury to organs around the liver: Other organs around the liver, such as the gallbladder, lung, or small bowel, may be injured accidentally during the biopsy.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Are Autopsy and Biopsy exactly the same thing?
No. An autopsy is an after the death of a dead person. A biopsy is tissue removal so different cells can be continued to functioning and alive.
Does scraping off tissues during a biopsy spread cancer?
No, Biopsies performed by IR specialists are finished with safety measures. Most serious injuries are cauterized or closed. A biopsy is not something to be scared of. It is fundamental in saving your life.
How long does it take to heal after a liver biopsy?
A liver biopsy is a procedure that includes taking a little piece of liver tissue for assessment with a microscope for signs of damage or disease. Full recovery in 1 to 2 days.
What type of anesthesia is used for a liver biopsy?
Local anesthesia is applied to the area where the biopsy needle will be inserted.
Does liver biopsy leave a scar?
The liver biopsy procedure leaves a very tiny scar.
What would a liver ultrasound be able to show?
Ultrasound is a front-line diagnostic tool for assessing the liver. It can assess the presence of liver infection (like Fatty liver), detect liver lesions, and much more.
About the Author:

Name: DR .SURESH GIRAGANI
INTERVENTIONAL RADIOLOGIST
DR. SURESH GIRAGANI CONSULTANT INTERVENTIONAL RADIOLOGIST at Yashoda group of hospitals has more than sixteen years of clinical experience in vascular interventions with a special interest in neurovascular and peripheral vascular disease interventional procedures.