
What Are Uterine Fibroids and what is the best treatment?

What are Uterine fibroids?
Fibroids are tumors that develop in the wall of the womb. They are typically benign (non-cancerous) growth of the uterus that mainly appear in women of childbearing (30-40 years old) but they can affect people of any age. Uterine fibroids are the most common benign tumor in women of reproductive age and represent one of the most common gynecological conditions. Uterine fibroids are also called as myomas or leiomyomas.
They can be minuscule and happen uniquely or become very huge and create in various areas. A few fibroids stay inside the mass of the uterus while others swell internal toward the womb or undertaking outward from the uterine wall. Fibroids can likewise become pedunculated or hang from a tail inside or outside of the uterus.
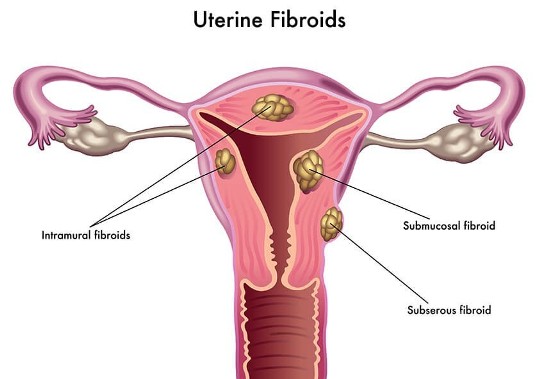
What are the different types of uterine fibroids?
Depending upon their growth in the Uterus. Fibroids are classified into 3 types they are:
- Submucosal: Which grows under the uterus lining or cavity and most likely symptomatic also associated with infertility.
- Intramural: Which grows in the uterine wall may cause enlarged uterus.
- Subserosal: This grows on the outside of the uterus.
What symptoms occur with uterine Fibroids?
- Heavier prolonged menstrual bleeding, sometimes with the passage of blood clots and leads to anemia.
- Pain, Pressure or feeling of fullness in the pelvis, abdomen or lower back.
- Longer than usual menstrual period that is for 7 days or more
- Frequent Urination or Constipation
- Pain during or bleeding after intercourse
- Infertility or Miscarriage
- Abnormally enlarged abdomen
- Bladder pressure leading to a constant urge to urinate
These can be asymptomatic and symptomatic. Many women might have uterine fibroids at some point during their lives however they don’t realize they have uterine fibroids as they cause no symptoms. Interventional Radiology Specialists might discover fibroids incidentally during a pelvic exam or prenatal ultrasound.
What are the causes of Uterine Fibroids?
The actual uterine fibroids causes are unknown. Their development might be connected with the individual’s estrogen levels.
- Hormonal changes – Estrogen and progesterone, two hormones that stimulate the improvement of the uterine lining during each monthly cycle in anticipation of pregnancy, seem to advance the development of fibroids.
- Family History – Fibroids might run in the family. If your mother, sister, or grandmother has a past filled with this condition, you might develop it too.
- Other development factors – Substances that assist the body with keeping up with tissues, for example, insulin-like development factors, may influence fibroid development.
- Pregnancy builds the creation of estrogen and progesterone in your body. Fibroids might create and develop quickly while you’re pregnant
How is Uterine Fibroids Diagnosed?
Uterine fibroids are diagnosed by some common types of imaging techniques.
They are:
- Ultrasonography
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
- CT Scan
- X-Ray
What is the best interventional treatment for uterine fibroids?
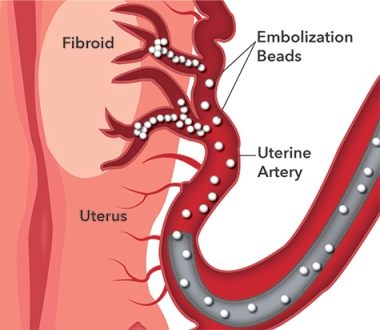
Surgery is not required in the majority of cases. The latest most advanced treatment is uterine artery embolization (UAE Embolization) or Uterine Fibroid embolization(UFE) performed by an interventional radiologist with the help of imaging guidance.
Why Interventional Radiology treatment best suits for treating uterine fibroids?
Interventional Radiology treatments are generally easier for the patient than surgery because they involve no surgical incision, less pain and short hospital stays.
What are some common uses of the UAE procedure?
Uterine artery embolization has been utilized for quite a long time to stop extreme pelvic bleeding caused by:
- trauma
- malignant gynecological tumors
- hemorrhage after childbirth
Uterine fibroid embolization is a specific type of UAE for treating suggestive fibroids.
Treating Fibroids with Uterine Artery Embolization (UAE):
Uterine artery embolization (also called uterine fibroid embolization or UFE) is a minimally invasive treatment for uterine fibroids. The Interventional Radiologist makes a small nick in the groin with a needle and inserts a catheter into an artery. The catheter is guided through an artery to the uterus while the interventional radiologist watches the progress of the procedure using real-time X-Ray (fluoroscopy). The Interventional radiologist injects tiny plastic particles the size of grains of sand into the artery that is supplying blood to the fibroid tumor this cuts off the blood flow and causes the tumor (or tumors) to shrink.
What are the Advantages of a uterine artery embolization?
- Treats all Fibroids simultaneously.
- Minimally Invasive, complications in frequent.
- Recurrence of treated fibroids rare.
- Short Recovery Period than surgery
- No scar formation
Must Read: The Ultimate Guide to Aneurysm Coiling
What are the risks of a uterine artery embolization?
Any procedure can have complications. Possible complications of this procedure include:
- Abnormal bleeding (hemorrhage)
- Injury to the uterus
- Infection of the uterus or the puncture site in the groin
- Collection of blood under the skin (hematoma) at the puncture site in the groin
- Injury to the artery being used
- Blood clots
- Infertility
- Loss of menstrual periods (amenorrhea)
Some women have post embolization syndrome. Symptoms include:
- Pelvic pain and cramping
- Nausea and vomiting
- Low-grade fever
- Fatigue and discomfort
What are the limitations of Uterine Artery Embolization (UAE)?
Uterine fibroid embolization should not be performed in ladies who have no side effects from their fibroid growths, when the disease is possible, or when there is inflammation or infection in the pelvis. Uterine fibroid embolization isn’t a possibility for ladies who are pregnant. A lady who is known to be seriously adversely affected by contrast materials that contain iodine requires pretreatment before UFE so choose an alternative treatment choice.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1 . What is the success rate of UAE?
Studies show that after 5 years about 80% of women who have had a UAE continue to experience significant (or) total relief of heavy bleeds, pain and other symptoms.
2. Is general anesthesia required for UAE?
No, UFE doesn’t need general anesthesia. The method is performed under local anesthesia with the patient conscious, but sedated, and feeling no pain.
3. How long does it take to recover from uterine fibroid embolization?
Many women resume light activities in a few days and the majority of women are able to recover to normal activities within one week to 10 days.
4. Do fibroids grow back after UAE?
No, Women’s fibroids usually do not grow back after they receive this UAE Treatment.
5. Will I still get my period after having a Uterine Fibroid Embolization (UFE)?
Yes, 90% of ladies really do notice a difference with their period stream during the first monthly cycle following a UFE method.
6. Can I still get pregnant after having a Uterine Fibroid Embolization (UFE)?
There have not been an adequate number of examinations to show the specific rate or direct connection of UFE procedures and their effect on fertility. The outcomes are changed and rely upon the age of the women, the extent of fibroids that were treated, and whether the woman is of advanced age and closer to menopause.
About the Author:

Name: DR .SURESH GIRAGANI
INTERVENTIONAL RADIOLOGIST
DR. SURESH GIRAGANI CONSULTANT INTERVENTIONAL RADIOLOGIST at Yashoda group of hospitals, has more than sixteen years of clinical experience in vascular interventions with a special interest in neurovascular and peripheral vascular disease interventional procedures.