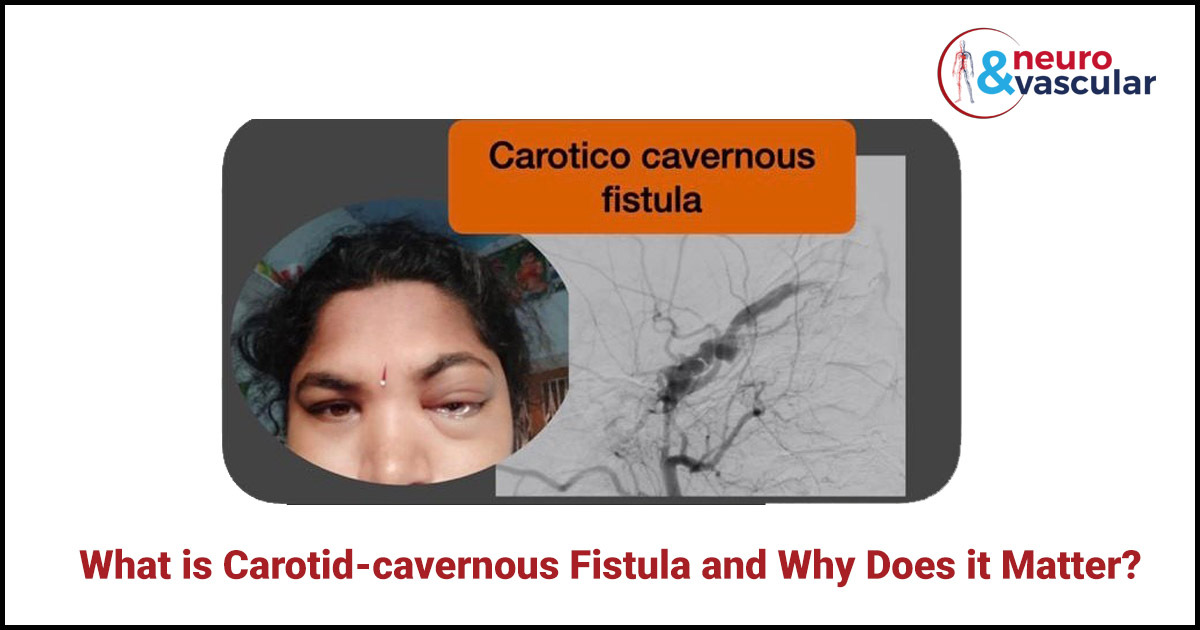
What is Carotid Cavernous Fistula and Why Does it Matter?
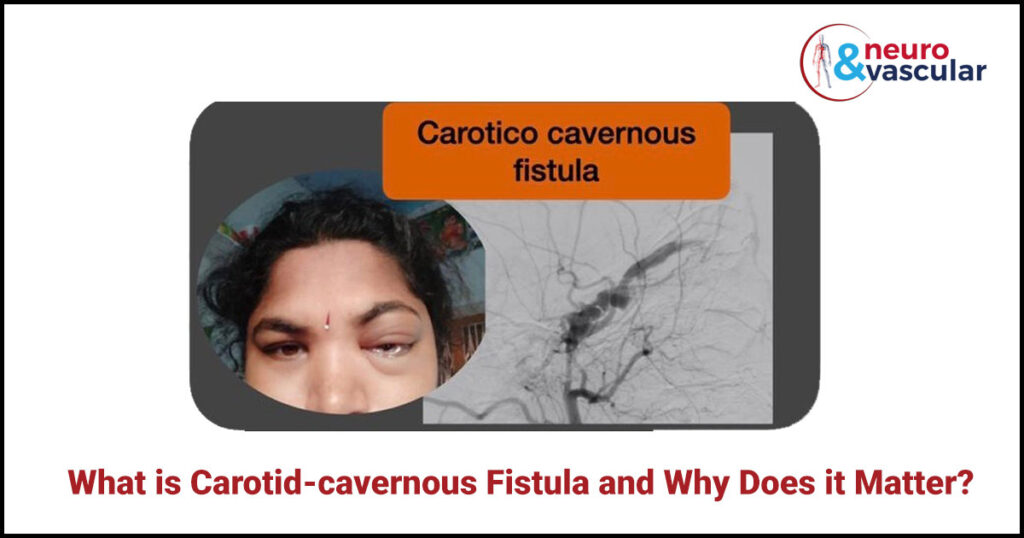
Carotid Cavernous Fistula:
What Is a Carotid Cavernous Fistula?
A carotid cavernous fistula (CCF) is the result of an abnormal vascular connection between the carotid artery( a major artery supplying blood to the brain) and the cavernous sinus located behind your eyes. If the carotid artery tears or develops a hole near the veins in the cavernous sinus area, a fistula (channel or shunt) creates, which permits bloodstream from the artery to the vein resulting in consequent symptoms.
Symptoms of CCF:
A CCF results in an increase in pressure in the cavernous sinus which compresses the nearby nerves that control eye movements and sensations in parts of your head and face. It can likewise influence the veins that drain the eyes. CCFs are one of the reasons for “red-eye” and other visual issues, including vision loss, if not diagnosed and treated in time.
Symptoms are as follows :
- Drooping of eyelid/ closed eye
- Bulging eye with congestion
- Double vision
- Blood flow sounds around your eye
- Red Eyes
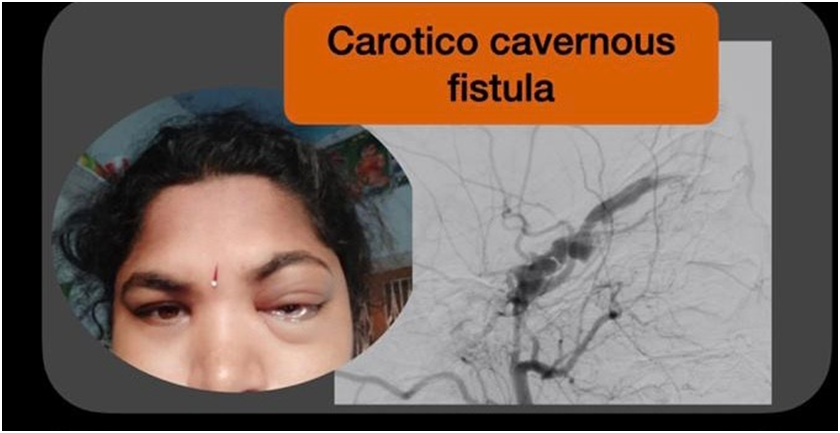
A 35 year lady had a left eye bulge, redness, congestion due to carotid cavernous fistula.
There are two types of Carotid Cavernous Fistulas:
- Direct CCF
- Indirect CCF
Direct CCF:
Direct CCF is due to a tear or hole in the carotid artery that directly creates communication between the cavernous sinus and the carotid artery. This hole is called a fistula, and it is usually caused by accident or injury. 70 to 90% of direct CCFs are caused by injury to Skull.
Indirect CCF:
Indirect CCFs occur spontaneously and can be caused by irregular connections between the carotid artery and the cavernous sinus. Indirect CCFs happen more frequently in postmenopausal women who have high blood pressure.
Causes for Carotid Cavernous Sinus Fistula:
Causes for Direct CCF:
- Being Hit in the Head
- Motor Vehicle Accident
- Surgery
- Infection
- Ruptured aneurysm
Diagnosis for Carotid Cavernous Fistula:
Diagnosing a carotid-cavernous fistula begins with an ocular examination. Your specialist could order imaging scans to examine your eye, near blood vessels and the cavernous sinus area.
Diagnosis tests include:
- MRI or Computerized tomography (CT) scan:
MRI or CT scans classically show an enlarged superior ophthalmic vein cavernous sinus enlargement.
- Cerebral Angiogram:
A cerebral angiogram is a catheter angiographic examination of blood vessels supplying your brain. It depicts the point of communication of the fistula between the carotid artery and the cavernous sinus, thereby helping plan the endovascular treatment.
Treatment for Carotid Cavernous Fistula :
The definitive treatment of a carotid-cavernous fistula (CCF) is indicated in most cases, as neglecting a CCF can result in blindness/ decreased vision, or sometimes bleeding/ hemorrhage in the brain. The treatment method relies upon the seriousness of the clinical symptoms, its angiographic attributes, and the danger it presents for intracranial hemorrhage. In most cases, endovascular treatment is preferred.
Endovascular embolization:
Endovascular embolization is the most widely recognized treatment for CCF. In this methodology, an interventional radiologist embeds a minuscule tube/ catheter into an artery in your groin and afterward directs it up to the fistula in the brain under fluoroscopy guidance. Platinum coils or different liquid embolic materials will be injected through the catheter, which will be placed exactly at the fistulous connection, consequently, the abnormal communication/ fistula will be closed and all the symptoms will be relieved. It’s a minimally invasive treatment, which doesn’t require cuts/ sutures on the head or eyes. Most of the time, the patient will be needed to stay in the hospital only for a couple of days. The treatment effect starts instantly and eye symptoms will resolve completely in 1-2 weeks’ time.
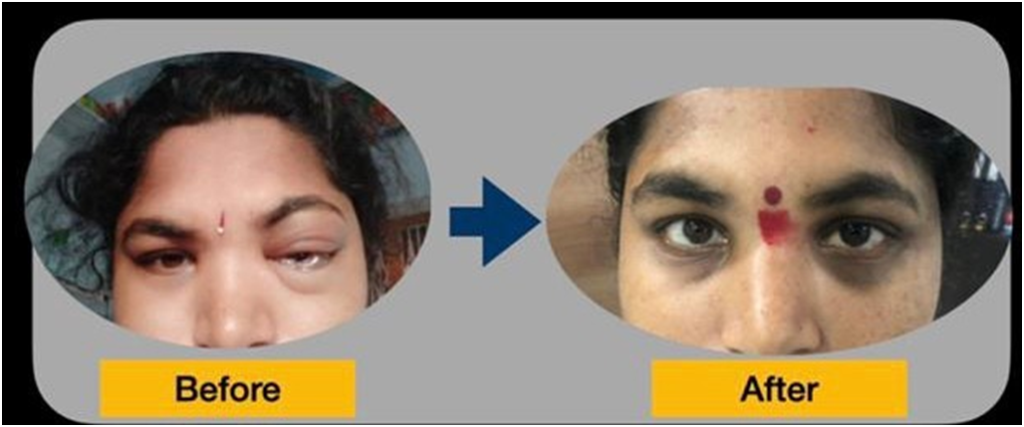

The left eye bulge, redness, and congestion due to carotid-cavernous fistula shows complete resolution after embolization.
About the Author:

Name: DR . SURESH GIRAGANI
INTERVENTIONAL RADIOLOGIST
DR. SURESH GIRAGANI CONSULTANT INTERVENTIONAL RADIOLOGIST at Yashoda group of hospitals has more than sixteen years of clinical experience in vascular interventions with a special interest in neurovascular and peripheral vascular disease interventional procedures.