Prostate Artery Embolization vs. Traditional BPH Treatment: Navigating the Choice for Prostate Health
The management of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), or an enlarged prostate, has witnessed significant advancements in recent years. Two prominent approaches are present – Prostate Artery Embolization (PAE) and traditional BPH treatments such as Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP) and medications. BPH is a prevalent problem in old age men over 50, with poor urine flow, frequent urination, and incomplete bladder emptying are some symptoms of noncancerous enlargement of the prostate gland. In this blog, we will explore these options, comparing their benefits, drawbacks, and helping you navigate the choice for optimal prostate health.
Symptoms of Benign prostatic hypertrophy (BPH):
The prostate is a walnut-sized organ in the male reproductive system that can enlarge and put pressure on the bladder and urethra, causing urinary side effects symptoms such as:
- Dribbling at the end of urination
- Straining
- Trouble emptying the bladder
- Frequent and urgent need to urinate
- Weak urine stream
- Blood in the urine
- UTIs (urinary tract infections)
- Can cause urinary bladder and kidney stones
Understanding BPH and Treatment Options:
Traditional BPH Treatments:
1. Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP):
TURP has long been a standard surgical procedure for BPH. It involves the removal of excess prostate tissue to alleviate urinary symptoms. While effective, TURP is an invasive surgery that may be associated with complications such as bleeding, infection, and a longer recovery period.
2. Medication (Alpha-Blockers and 5-Alpha Reductase Inhibitors):
Medications are often prescribed to manage BPH symptoms. Alpha-blockers relax the muscles around the prostate, improving urine flow, while 5-alpha reductase inhibitors shrink the prostate. However, medications may come with side effects, and their efficacy can vary from person to person.
Prostate Artery Embolization (PAE):
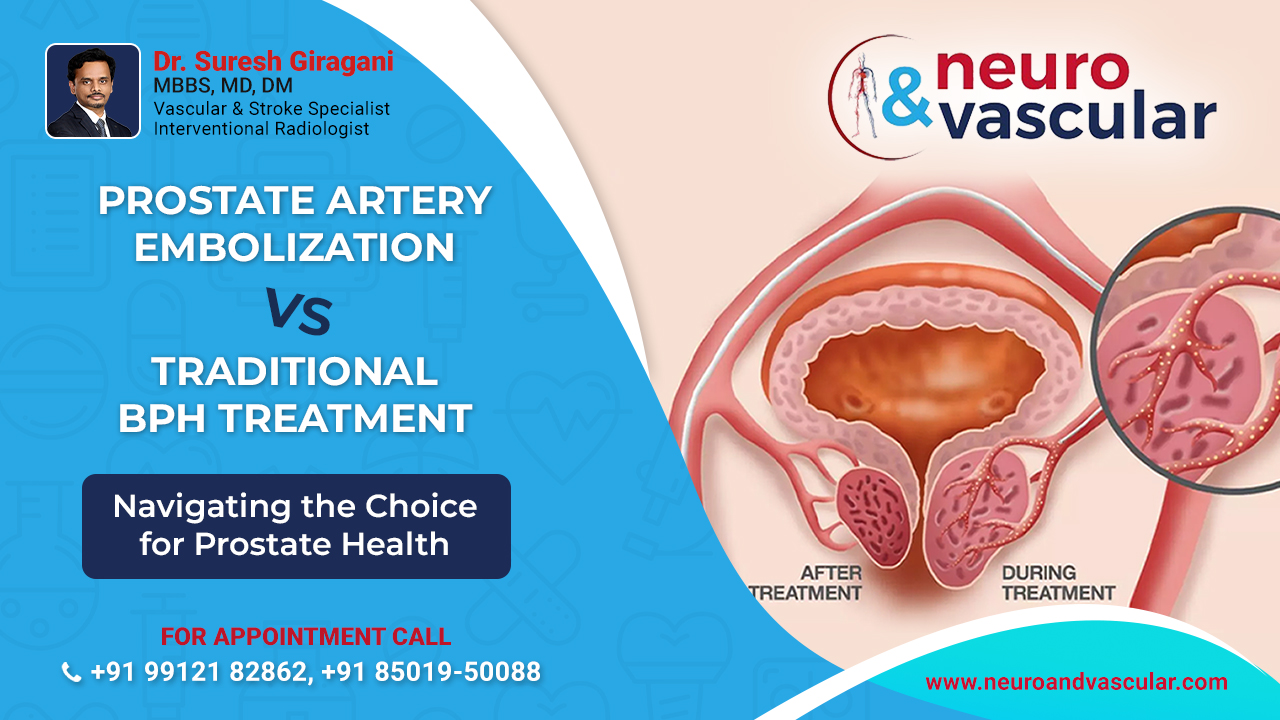
Prostate Artery Embolization (PAE) emerges as a hopeful remedy for individuals grappling with an enlarged prostate or benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). If you are a male aged 50 or older, the likelihood of experiencing BPH-related challenges increases. BPH entails the enlargement of the prostate gland, giving rise to discomfort and various associated symptoms. To opting for surgical intervention, interventional radiologists employ vascular catheters to administer minute particles to the affected area. This process diminishes blood flow, leading to a reduction in the size of the prostate. The PAE procedure is tailored to the specific conditions of each patient, offering a personalized approach to reclaiming a life unhindered by the effects of BPH.
1. Minimally Invasive Nature:
PAE is a minimally invasive procedure that avoids the need for major surgery. It is performed by selectively blocking the blood vessels supplying the prostate, leading to a reduction in prostate size. This targeted approach minimizes the risks associated with traditional surgical interventions.
2. Preservation of Sexual Function:
Unlike some traditional treatments that may impact sexual function, PAE is designed to specifically target the blood vessels supplying the prostate, reducing the risk of damage to nerves involved in sexual health.
Outpatient Procedure and Shorter Recovery Time:
PAE is typically performed on an outpatient basis, allowing patients to return home the same day. The recovery time associated with PAE is generally shorter compared to traditional surgical options, enabling a quicker return to normal activities.
1. Customizable Approach:
PAE is a customizable procedure that takes into account the individual characteristics of each patient’s prostate. Factors such as size, shape, and symptoms are carefully considered to optimize outcomes.
2. Choosing the Right Approach:
The choice between Prostate Artery Embolization and traditional BPH treatments depends on various factors, including the patient’s overall health, the size of the prostate, and personal preferences.
3. Severity of Symptoms:
For men with severe symptoms and larger prostates, traditional surgical interventions like TURP may be a more suitable option. However, for those seeking a less invasive alternative with a quicker recovery, PAE may be the preferred choice.
4. Desire for Minimally Invasive Options:
Men who prefer minimally invasive procedures and want to avoid the risks associated with major surgery may find PAE to be a more attractive option.
5. Preservation of Sexual Function:
If the preservation of sexual function is a significant concern, PAE offers an advantage over some traditional treatments.
How Prostate Artery Embolization is done?
Prostate Artery Embolization involves the selective blocking of blood vessels that supply the prostate. By reducing blood flow to the prostate, PAE aims to shrink the gland, alleviating the urinary symptoms associated with BPH. The procedure is performed through a small incision, making it a minimally invasive alternative to traditional surgical interventions.
Patients considering or having undergone PAE should engage in open and transparent discussions with their healthcare providers. Regular follow-up assessments will help in assessing the ongoing effectiveness of the PAE and determining the need for any additional interventions. The possibility of repeating PAE highlights the commitment of medical professionals to personalized and effective care, ensuring that individuals with BPH can continue to enjoy an improved quality of life.
Conclusion:
The decision between Prostate Artery Embolization and traditional BPH treatments is a highly individual one. Consulting with interventional radiologist is crucial to determine the most appropriate approach based on the specific characteristics of the enlarged prostate, the severity of symptoms, and the patient’s overall health. Both PAE and traditional treatments have their merits, and the choice ultimately depends on a careful consideration of the unique circumstances of each patient. As the field of interventional radiologist continues to evolve, men now have a range of options to address BPH, allowing for a more personalized and effective approach to prostate health.
About the Author:

Name: DR . SURESH GIRAGANI
INTERVENTIONAL RADIOLOGIST
DR. SURESH GIRAGANI CONSULTANT INTERVENTIONAL RADIOLOGIST at Apollo hospitals Jubilee Hills has more than sixteen years of clinical experience in vascular interventions with a special interest in neurovascular and peripheral vascular disease interventional procedures.