
World Stroke Day 2022: Minutes Can Save Lives

A stroke can happen to anyone, at any time, anywhere. According to the World Stroke Organization, stroke is the second leading cause of death and disability worldwide, but many strokes are preventable. Action taken within minutes can save lives.
Every year on October 29th, World Stroke Day is observed. This year’s Theme for World Stroke day 2022 is Minutes Can Save Lives.
The World Stroke Organization (WSO) established this global awareness day in 2006. It provides a global platform to raise awareness of the serious threat and high rates of stroke, as well as to discuss how we can do better in the future by increasing public awareness of stroke risk factors and symptoms. World Stroke Day is also an opportunity to advocate for global decision-makers to take action to improve stroke prevention, access to acute treatment, and support for survivors and caregivers
The prevalence of stroke has already reached epidemic proportions. One in every 4 adults over the age of 25 will suffer a stroke in their lifetime. Current trends suggest that the number of annual deaths will soon exceed 6.7 million if appropriate action is not taken.

In 2021 and 2022, the World Stroke Day #Precioustime campaign will focus on raising awareness of stroke symptoms and the importance of timely access to quality stroke treatment, as well as recognizing and treating stroke warning signs so that its devastating consequences can be prevented.
One of the most important things to do in observance of World Stroke Day is to learn more about this disease, its causes, prevention and treatments.
Facts about Stroke:
- Stroke risk increases with age. Nearly ¾ of strokes happen to people over age 65. However, even it is essential that older people are aware of healthy options for stroke prevention, younger people should be aware that too can be affected by a stroke.
- A doctor should track risk factors for stroke. These may include high blood pressure, diabetes, obesity, high cholesterol, and smoking.
- More women die of strokes than men. In fact, twice as many women die of stroke each year than die of breast cancer.
- Stroke risk increases with age, but strokes can occur in young adults, children, and even unborn babies.
- 3 out of every 4 people who suffer their first stroke have high blood pressure.
- If one of your parents had an ischemic stroke before 65, you’re at 3 times the risk of suffering one yourself.
- Stroke is largely treatable, thanks to clot-busting drugs and medical devices. But every second counts. The faster you’re treated, the more likely you are to recover without permanent disability.
What is a stroke?
A stroke occurs when a blood vessel brings blood to the brain and gets blocked or ruptures.
This means the brain can’t get the oxygen and nutrients it needs, and without oxygen and nutrients, nerve cells can’t function. Your brain controls your ability to move, feel, think and behave. A brain injury from a stroke could affect any or all of these functions.
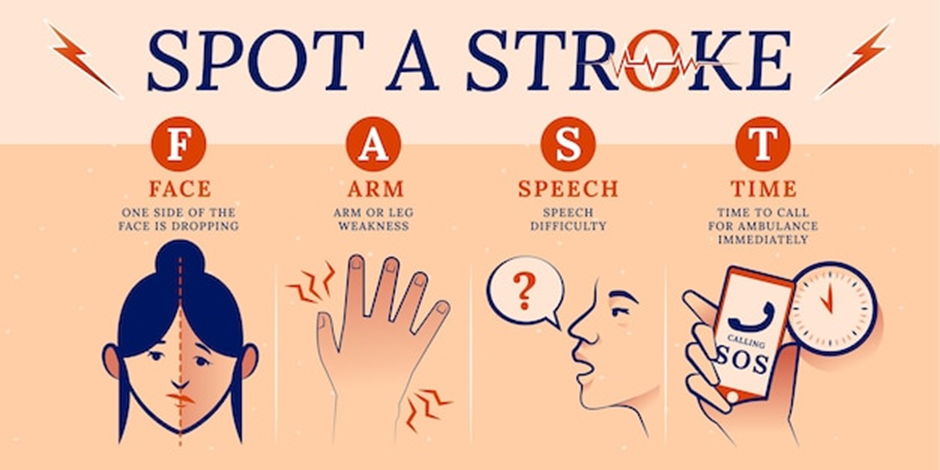
How to Recognize a Stroke?
The acronym F.A.S.T can help you remember these signs:
F: Face drooping
A: Arm Weakness
S: Speech Difficulty
T: Time for specialist treatment
If anyone observes the above symptoms seek medical help ASAP
Types of stroke:
There are several types of stroke: ischemic stroke and hemorrhagic stroke and Transient Ischemic Stroke.
Ischemic stroke occurs when a blood vessel that supplies blood to the brain is blocked by a blood clot.
A hemorrhagic stroke occurs when a blood vessel in part of the brain becomes weak and bursts open, causing blood to leak into the brain.
Transient Ischemic Stroke: This stroke is also known as Mini- Stroke as it is a temporary decrease in the Blood Supply to the parts of the brain due to a clot.
What are the Risks factors for stroke?
- Smoking
- Obesity
- Medications
- Heart disease
- Physical inactivity
- Stress
- Alcohol
- High Blood pressure
- Diabetes
- High blood cholesterol
- Difficulty walking
What happens after a Stroke?
A stroke can result in temporary or permanent disabilities, depending on how long parts of the brain were deprived of blood supply.
1. Memory Loss
2. Paralysis
3. Suffering from depression
4. Numbness
5. Behavioural Changes
6. Problems in talking
Advanced Treatment Options for Stroke?
Thrombolysis:
A drug called tissue plasminogen activator, often known as “tPA,” is injected into a vein to break up a clot that may be limiting blood flow to the brain. When taken intravenously (IV), the therapy should be given within 4.5 hours of the onset of symptoms. A quick tPA treatment not only increases a person’s chances of survival but also reduces complications. To restore blood flow, tPA destroys the blood clot. A catheter, which is a long, thin tube inserted into an artery in the groin and gradually advanced to the brain to inject tPA directly at the site of the stroke, can sometimes be used to deliver tPA directly into the brain.
The time window for this treatment is also limited, however, it is slightly longer than with injectable tPA. If the patient had an acute ischemic stroke or The Patient is not eligible or has failed in intravenous thrombolysis then mechanical thrombectomy could be a great option and the mechanical thrombectomy treatment is performed by An Interventional Radiologist based on age, Severity of stroke, time window and Test results. In selected patients with stroke, an interventional procedure known as “Mechanical Thrombectomy” can be used to remove the clot from an occluded blood vessel within the first 6 to 24 hours
Mechanical Thrombectomy:
When the brain starves out due to oxygen deficiency, massive tissue damage occurs leading to a medical emergency, i.e. stroke. An ischemic stroke usually occurs due to the clogging of a brain blood vessel (artery) by a clot that stops the blood supply to the brain.
However, it is possible to reverse the damage to a certain extent by doing a timely mechanical thrombectomy for acute ischemic stroke. Mechanical thrombectomy helps in removing the clot from the artery supplying blood to the brain.
How is Mechanical thrombectomy performed?
For large blood clots, mechanical thrombectomy was performed with hollow suction tubes and a clot-retrieving mesh (stent retriever).
In this process, a catheter bearing a stent retriever is introduced beyond the site of blood occlusion using X-ray imaging. . The stent is allowed to expand, engage the clot and pulled out, thereby, removing the clot. This results in the restoration of the blood flow to the oxygen-deficient brain area.
The success rate of mechanical thrombectomy is higher than any other procedure for ischemic stroke. It often provides immediate effects and helps in reviving the damaged cells. And some patients have recovery on the procedure table itself. However, the recovery may be slow in other patients, with continuing improvement up to 3 months.
Stroke Prevention Steps:
Most strokes can be preventable with a few simple steps. Here are the top tips that help to reduce our risk of stroke.
- Control High Blood Pressure
- Exercise 5 times per week
- Eat a healthy Balanced diet
- Reduce your cholesterol
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Stop smoking and avoid smoking environments
- Reduce your Alcohol Intake
- Identify and treat atrial fibrillation
- Manage diabetes
- Manage stress & depression
Conclusion:
When somebody has a stroke, every second that goes by is crucial. As brain tissue and millions of neurons begin to fade away, time could not be more precious. This world stroke day, we hope our attempt at knowledge on stroke will help you or your loved ones. Moreover, if you have any concerns about stroke or are looking for prevention or therapies, Our Interventional Radiology Specialist will answer your queries.
About the Author:

Name: DR . SURESH GIRAGANI
INTERVENTIONAL RADIOLOGIST
DR. SURESH GIRAGANI CONSULTANT INTERVENTIONAL RADIOLOGIST at Apollo hospitals Jubilee Hills has more than sixteen years of clinical experience in vascular interventions with a special interest in neurovascular and peripheral vascular disease interventional procedures.